Management System
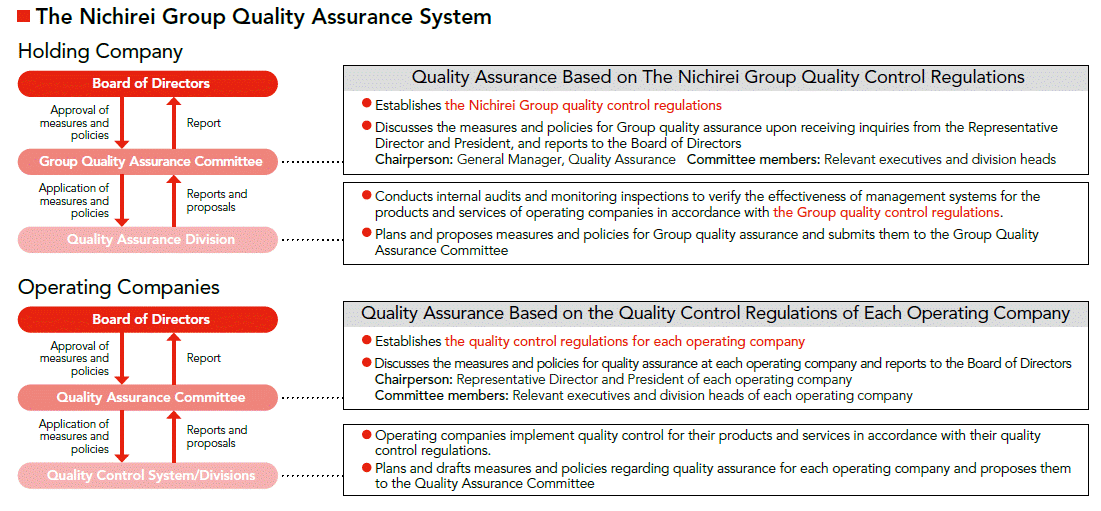
The Nichirei Group Quality Assurance System Diagram
Nichirei Corporationʼs Quality Assurance Division has established rules and standards for quality control and quality assurance and performs internal audits and monitoring inspections based on quality management standards to ensure that the Groupʼs quality management system is functioning effectively.
Each operating companyʼs Quality Assurance Division performs quality inspections of its own products and services and reports and shares its implementation status with the Quality Assurance Committee and the Group Quality Assurance Committee, which assists with the further revision and enhancement of its quality assurance system.
Control Standards
In addition to promoting the management of internal rules and the introduction of appropriate international standards, we are strengthening our quality control system to ensure we continue to provide safe products and services.
International Standards (Partial List)
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 (quality management system) |
The most widely adopted management system certification, used by over one million organizations in more than 170 countries. |
| HACCP system, Codex Alimentarius, General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969, CAC/RCP 1-1969) |
Food production process-related international hygiene standards to prevent harm by conducting risk analysis and setting up critical management points. |
| ISO 22000 | International food safety standard to curb food safety risks based on HACCP food hygiene management methods. |
| Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI)- approved food safety manegement systems (FSMS) |
Scheme approved on the basis of food safety requirements, such as FSSC 22000 and JFS-C standards. |
Educating Employees for Better Quality
To inculcate an awareness of quality assurance in the Quality Assurance Division and among all Group employees, we provide annual e-learning opportunities focused on quality assurance. We regularly share information on incidents and case studies pertaining to quality assurance, using easily understandable illustrations and humorous Japanese poems.
Further, we conduct topical training once a year to improve the competencies of quality assurance personnel.
The topical training includes the explanation of requirements related to the prevention of food mislabeling, and support for the creation of remote-auditing rules.
Moreover, quality assurance personnel visit production facilities in order to deepen their understanding of quality through hygiene-management training and worksite dialogues. We also have incorporated remote training and discussions, enabling Nichirei to expand the scope of training to include the participation of even more people.

Employees attend a training session on hygiene management at a production facility in Japan.
