About Antifreeze Proteins (AFPs)
About AFPs
AFPs, including antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) are proteins found in fish, insects, plants, microorganisms, and other living things that exist in low-temperature environments.
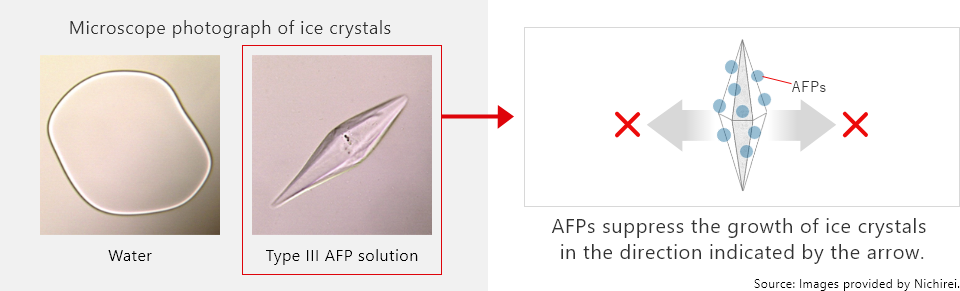
These proteins lower the temperature at which an organism freezes and contribute to maintaining the organism’s life by preventing freezing and the recrystallization of ice crystals.
Antifreeze proteins bond strongly to the surface of innumerable microscopic ice crystals that form in water at the moment of freezing and suppress their growth. Normally, ice crystals that form in an aqueous solution grow from a disk into an elliptical shape, but antifreeze proteins adhere to the ice and change the shape of the ice crystals. Even if the temperature is lowered only slightly, the size of the ice crystals remains nearly unchanged.
In addition, the AFPs inside fish have been observed as resulting in prolonged cell life, leading to the discovery that AFPs attach to the lipid bilayer membrane.
For some time, Nichirei has collaborated with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) to promote the development of technologies for efficiently extracting antifreeze proteins from fish.
There are several types of fish AFPs that differ in amino acid composition and three-dimensional structure, and each has different ice crystal and cellular properties.
Types of AFPs in Fish
| Types of fish with AFPs | Amino acid sequence characteristics | 33D structure | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFGPs Mw = 2,600-33,000 |
Emerald Rockcod 
Notothenioidei, Codidae |
Repeated disaccharide-modified alanine-alanine-threonine |
Undecided Predicts polyproline II helix structure |
| Type I AFP Mw = 3,300-4,500 |
Winter Flounder 
Flatfish, Cottidae |
Comprising repeating units of Thr-X10 (X is mainly Ala) |
 Referred to as α-helices structures |
| Type II AFP Mw = 14,000-24,000 |
Atlantic Herring 
Clupeidae, Osmeridae, Hemitripteridae |
High affinity with sugar chain recognition domain of Ca2+-dependent lectins |
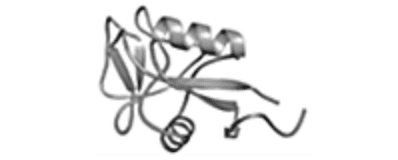 Stabilized by S-S bond |
| Type III AFP Mw = 6,500-7,000 |
Ocean Pout 
Eelpoutaceae |
Comprise various amino acids Many do not contain S-S bonds |
 Includes beta-sandwich structure |
